Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
天野 由記; Sachdeva, R.*; Gittins, D.*; Anantharaman, K.*; Lei, S.*; Valentin-Alvarado, L. E.*; Diamond, S.*; 別部 光里*; 岩月 輝希; 望月 陽人; et al.
Environmental Microbiome (Internet), 19, p.105_1 - 105_17, 2024/12
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Genetics & Heredity)Underground research laboratories (URLs) provide a window on the deep biosphere and enable investigation of potential microbial impacts on nuclear waste, CO and H
and H stored in the subsurface. We carried out the first multi-year study of groundwater microbiomes sampled from defined intervals between 140 and 400 m below the surface of the Horonobe and Mizunami URLs, Japan. The Horonobe and Mizunami microbiomes are dissimilar, likely because the Mizunami URL is hosted in granitic rock and the Horonobe URL in sedimentary rock. Despite this, hydrogen metabolism, rubisco-based CO
stored in the subsurface. We carried out the first multi-year study of groundwater microbiomes sampled from defined intervals between 140 and 400 m below the surface of the Horonobe and Mizunami URLs, Japan. The Horonobe and Mizunami microbiomes are dissimilar, likely because the Mizunami URL is hosted in granitic rock and the Horonobe URL in sedimentary rock. Despite this, hydrogen metabolism, rubisco-based CO fixation, reduction of nitrogen compounds and sulfate reduction are well represented functions in microbiomes from both URLs, although methane metabolism is more prevalent at the organic- and CO
fixation, reduction of nitrogen compounds and sulfate reduction are well represented functions in microbiomes from both URLs, although methane metabolism is more prevalent at the organic- and CO -rich Horonobe URL. We detected near-identical genotypes for approximately one third of all genomically defined organisms at multiple depths within the Horonobe URL. This cannot be explained by inactivity, as in situ growth was detected for some bacteria, albeit at slow rates. Given the current low hydraulic conductivity and groundwater compositional heterogeneity, ongoing inter-site strain dispersal seems unlikely. Alternatively, the Horonobe URL microbiome homogeneity may be explained by higher groundwater mobility during the last glacial period. Genotypically-defined species closely related to those detected in the URLs were identified in three other subsurface environments in the USA. Thus, dispersal rates between widely separated underground sites may be fast enough relative to mutation rates to have precluded substantial divergence in species composition. Species overlaps between subsurface locations on different continents constrain expectations regarding the scale of global subsurface biodiversity. Overall, microbiome and geochemical stability over the study period has important implications for underground storage applications.
-rich Horonobe URL. We detected near-identical genotypes for approximately one third of all genomically defined organisms at multiple depths within the Horonobe URL. This cannot be explained by inactivity, as in situ growth was detected for some bacteria, albeit at slow rates. Given the current low hydraulic conductivity and groundwater compositional heterogeneity, ongoing inter-site strain dispersal seems unlikely. Alternatively, the Horonobe URL microbiome homogeneity may be explained by higher groundwater mobility during the last glacial period. Genotypically-defined species closely related to those detected in the URLs were identified in three other subsurface environments in the USA. Thus, dispersal rates between widely separated underground sites may be fast enough relative to mutation rates to have precluded substantial divergence in species composition. Species overlaps between subsurface locations on different continents constrain expectations regarding the scale of global subsurface biodiversity. Overall, microbiome and geochemical stability over the study period has important implications for underground storage applications.
 archaea host diverse and interacting extrachromosomal elements
archaea host diverse and interacting extrachromosomal elementsShi, L.-D.*; West-Roberts, J.*; Schoelmerich, M. C.*; Penev, P. I.*; Chen, L.-X.*; 天野 由記; Lei, S.*; Sachdeva, R.*; Banfield, J. F.*
Nature Microbiology (Internet), 9(9), p.2422 - 2433, 2024/09
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:39.49(Microbiology)Methane emissions that contribute to climate change can be mitigated by anaerobic methane-oxidizing archaea such as  . Some
. Some  have huge extrachromosomal genetic elements (ECEs) called Borgs that may modulate their activity, yet the broader diversity of
have huge extrachromosomal genetic elements (ECEs) called Borgs that may modulate their activity, yet the broader diversity of  ECEs is little studied. Here, we report small enigmatic linear ECEs, circular viruses and unclassified ECEs, that we predict replicate within
ECEs is little studied. Here, we report small enigmatic linear ECEs, circular viruses and unclassified ECEs, that we predict replicate within  . The linear ECEs have features such as inverted terminal repeats, pervasive tandem repeats, and coding patterns that are strongly reminiscent of Borgs, but they are only 52 kb to 145 kb in length. They share proteins with Borgs and
. The linear ECEs have features such as inverted terminal repeats, pervasive tandem repeats, and coding patterns that are strongly reminiscent of Borgs, but they are only 52 kb to 145 kb in length. They share proteins with Borgs and  . Thus, we refer to them as mini-Borgs. Mini-Borgs are genetically diverse and we assign them to at least five family-level groups. We also identify eight novel families of
. Thus, we refer to them as mini-Borgs. Mini-Borgs are genetically diverse and we assign them to at least five family-level groups. We also identify eight novel families of  viruses, some of which encode multiheme cytochromes, and unclassified circular ECEs that encode TnpB genes. A population-heterogeneous CRISPR array is encoded in close proximity to TnpB and has spacers that target other
viruses, some of which encode multiheme cytochromes, and unclassified circular ECEs that encode TnpB genes. A population-heterogeneous CRISPR array is encoded in close proximity to TnpB and has spacers that target other  ECEs including previously reported plasmids. The diverse groups of ECEs exchange genetic information with each other and with
ECEs including previously reported plasmids. The diverse groups of ECEs exchange genetic information with each other and with  , likely impacting the activity and evolution of these environmentally important archaea.
, likely impacting the activity and evolution of these environmentally important archaea.
Esser, S. P.*; Rahlff, J.*; Zhao, W.*; Predl, M.*; Plewka, J.*; Sures, K.*; Wimmer, F.*; Lee, J.*; Adam, P. S.*; McGonigle, J.*; et al.
Nature Microbiology (Internet), 8(9), p.1619 - 1633, 2023/09
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:74.53(Microbiology)CRISPR-Cas systems defend prokaryotic cells from viruses, plasmids, and other mobile genetic elements. Capitalizing on multi-omics approaches, we show here that the CRISPR-Cas systems of uncultivated archaea also play an integral role in mitigating potentially detrimental interactions with episymbionts. A comprehensive analysis of CRISPR-Cas-based infection histories revealed that uncultivated deep-subsurface archaeal primary-producers defend themselves from archaeal episymbionts of the DPANN superphylum of archaea, some of which are known to fuse their membranes with their host. We show that host cells counter these attacks by deploying one of two CRISPR-Cas systems (type I-B and type III-A) to target and disrupt essential genes in the episymbiont. However, genome-scale modeling of metabolic interactions between two deep subsurface host-symbiont systems revealed that host cells also benefit from the symbionts via metabolic complementation. We speculate that populations of these uncultivated archaeal episymbionts are currently transitioning from a parasitic lifestyle to one of mutualism, as must have occurred in countless mutualistic systems known today. By expanding our analysis to thousands of archaeal genomes, we conclude that CRISPR-Cas mediated resistance to archaeal episymbiosis evolved independently in various archaeal lineages and may be a wide-spread evolutionary phenomenon.
 archaea
archaeaSchoelmerich, M. C.*; Oubouter, H. T.*; Sachdeva, R.*; Penev, P. I.*; 天野 由記; West-Roberts, J.*; Welte, C. U.*; Banfield, J. F.*
Nature Communications (Internet), 13, p.7085_1 - 7085_11, 2022/11
被引用回数:13 パーセンタイル:72.26(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Anaerobic methanotrophic archaea (ANME) make energy from the breakdown of methane, an important driver of global warming, yet the extrachromosomal genetic elements that impact the activities of ANME are little understood. Here we describe large plasmids associated with ANME of the Methanoperedens Genus. These have been maintained in two enrichment bioreactors that are highly dominated by different  species and associate with
species and associate with  species in other anaerobic environments. By manual curation we show that two of the plasmids are large (155,607 bp and 191,912 bp), circular, and replicate bidirectionally. The group of
species in other anaerobic environments. By manual curation we show that two of the plasmids are large (155,607 bp and 191,912 bp), circular, and replicate bidirectionally. The group of  species that carry these plasmids is related to
species that carry these plasmids is related to  ,
,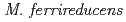 and
and 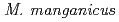 and the plasmids occur in the same copy number as the main chromosome. The larger plasmid encodes transporters that potentially enhance
and the plasmids occur in the same copy number as the main chromosome. The larger plasmid encodes transporters that potentially enhance  access to Ni, which is required for the MCR complex, Co required for the cobalamin cofactor needed for methyltransferases tied to central processes and amino acid uptake. We show that many plasmid genes are actively transcribed, including genes involved in plasmid chromosome maintenance and segregation, a Co
access to Ni, which is required for the MCR complex, Co required for the cobalamin cofactor needed for methyltransferases tied to central processes and amino acid uptake. We show that many plasmid genes are actively transcribed, including genes involved in plasmid chromosome maintenance and segregation, a Co /Ni
/Ni transporter and cell protective proteins. Notably, plasmid-borne genes for a ribosomal protein uL16 and adjacent elongation factor eEF2 are highly expressed. These are not encoded in the host
transporter and cell protective proteins. Notably, plasmid-borne genes for a ribosomal protein uL16 and adjacent elongation factor eEF2 are highly expressed. These are not encoded in the host  genome, indicating an obligate interdependence between this plasmid and its host. The finding of plasmids of
genome, indicating an obligate interdependence between this plasmid and its host. The finding of plasmids of  opens the way for the development of genetic vectors that could be used to probe little understood aspects of
opens the way for the development of genetic vectors that could be used to probe little understood aspects of  physiology. Ultimately, this may provide a route to introduce or alter genes that may enhance growth and overall metabolism to accelerate methane oxidation rates.
physiology. Ultimately, this may provide a route to introduce or alter genes that may enhance growth and overall metabolism to accelerate methane oxidation rates.
Jaffe, A. L.*; Thomas, A. D.*; He, C.*; Keren, R.*; Valentin-Alvarado, L. E.*; Munk, P.*; Bouma-Gregson, K.*; Farag, I. F.*; 天野 由記; Sachdeva, R.*; et al.
mBio, 12(4), p.e00521-21_1 - e00521-21_21, 2021/08
被引用回数:28 パーセンタイル:87.18(Microbiology)Candidate Phyla Radiation (CPR) bacteria are small, likely episymbiotic organisms found across Earth's ecosystems. Despite their prevalence, the distribution of CPR lineages across habitats and the genomic signatures of transitions amongst these habitats remain unclear. Hear, we expand the genome inventory for Absconditabacteria (SR1), Gracilibacteria, and Saccharibacteria (TM7), CPR bacteria known to occur in both animal-associated and environmental microbiomes, and investigate variation in gene content with habitat of origin. By overlaying phylogeny with habitat information, we show that bacteria from these three lineages have undergone multiple transitions from environmental habitats into animal microbiomes. Based on co-occurrence analyses of hundreds of metagenomes, we extend the prior suggestion that certain TM7 have broad bacterial host ranges and constrain possible host relationships for SR1 and Gracilibacteria. Full-proteome analyses show that animal-associated TM7 have smaller gene repertoires than their environmental counterparts and are enriched in numerous protein families, including those likely functioning in amino acid metabolism, phage defense, and detoxification of peroxide. In contrast, some freshwater TM7 encodea putative rhodopsin. For protein families exhibiting the clearest patterns of differential habitat distribution, we compared protein and species phylogenies to estimate the incidence of lateral gene transfer and genomic loss occurring over the species tree. These analyses suggest that habitat transitions were likely not accompanied by large transfer or loss events, but rather were associated with continuous proteome remodeling. Thus, we speculate that CPR habitat transitions were driven largely by availability of suitable host taxa, and were reinforced by acquisition and loss of some capacities.
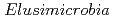 are metabolically diverse compared to gut microbiome
are metabolically diverse compared to gut microbiome 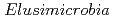 and some have a novel nitrogenase paralog
and some have a novel nitrogenase paralogM heust, R.*; Castelle, C. J.*; Matheus Carnevali, P. B.*; Farag, I. F.*; He, C.*; Chen, L.-X.*; 天野 由記; Hug, L. A.*; Banfield, J. F.*
heust, R.*; Castelle, C. J.*; Matheus Carnevali, P. B.*; Farag, I. F.*; He, C.*; Chen, L.-X.*; 天野 由記; Hug, L. A.*; Banfield, J. F.*
ISME Journal, 14(12), p.2907 - 2922, 2020/12
被引用回数:71 パーセンタイル:96.30(Ecology)We reconstructed 94 draft-quality, non-redundant genomes from diverse animal-associated and natural environments. Genomes group into 12 clades, 10 of which previously lacked reference genomes. Groundwater-associated 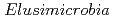 are predicted to be capable of heterotrophic or autotrophic lifestyles, reliant on oxygen or nitrate/nitrite-dependent respiration of fatty acids, or a variety of organic compounds and Rnf-dependent acetogenesis with hydrogen and carbon dioxide as the substrates. Genomes from two clades of groundwater-associated
are predicted to be capable of heterotrophic or autotrophic lifestyles, reliant on oxygen or nitrate/nitrite-dependent respiration of fatty acids, or a variety of organic compounds and Rnf-dependent acetogenesis with hydrogen and carbon dioxide as the substrates. Genomes from two clades of groundwater-associated 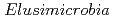 often encode a new homologous group of nitrogenase-like proteins that co-occur with an extensive suite of radical SAM-based proteins. We identified similar genomic loci in genomes of bacteria from the Gracilibacteria and Myxococcus phyla and predict that the gene clusters reduce a tetrapyrrole, possibly to form a novel cofactor. The animal-associated
often encode a new homologous group of nitrogenase-like proteins that co-occur with an extensive suite of radical SAM-based proteins. We identified similar genomic loci in genomes of bacteria from the Gracilibacteria and Myxococcus phyla and predict that the gene clusters reduce a tetrapyrrole, possibly to form a novel cofactor. The animal-associated 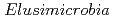 clades nest phylogenetically within two groundwater-associated clades. Thus, we propose an evolutionary trajectory in which some
clades nest phylogenetically within two groundwater-associated clades. Thus, we propose an evolutionary trajectory in which some 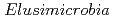 adapted to animal-associated lifestyles from groundwater-associated species via genome reduction.
adapted to animal-associated lifestyles from groundwater-associated species via genome reduction.
Al-Shayeb, B.*; Sachdeva, R.*; Chen, L.-X.*; Ward, F.*; Munk, P.*; Devoto, A.*; Castelle, C. J.*; Olm, M. R.*; Bouma-Gregson, K.*; 天野 由記; et al.
Nature, 578(7795), p.425 - 431, 2020/02
被引用回数:295 パーセンタイル:99.46(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Phage typically have small genomes and depend on their bacterial hosts for replication. We generated metagenomic datasets from many diverse ecosystems and reconstructed hundreds of huge phage genomes, between 200 kbp and 716 kbp in length. Thirty four genomes were manually curated to completion, including the largest phage genomes yet reported. Expanded genetic repertoires include diverse and new CRISPR-Cas systems, tRNAs, tRNA synthetases, tRNA modification enzymes, initiation and elongation factors and ribosomal proteins. Phage CRISPR have the capacity to silence host transcription factors and translational genes, potentially as part of a larger interaction network that intercepts translation to redirect biosynthesis to phage-encoded functions. Some phage repurpose bacterial systems for phage-defense to eliminate competing phage. We phylogenetically define seven major clades of huge phage from human and other animal microbiomes, oceans, lakes, sediments, soils and the built environment. We conclude that large gene inventories reflect a conserved biological strategy, observed across a broad bacterial host range and resulting in the distribution of huge phage across Earth's ecosystems.
Atz, M.*; Salazar, A.*; 平野 史生; Fratoni, M.*; Ahn, J.*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 124, p.28 - 38, 2019/02
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:33.76(Nuclear Science & Technology)使用済燃料を地層処分する場合を想定して(使用済燃料の直接処分)、処分場の周辺岩盤で燃料成分が蓄積することによって臨界が起こる可能性を評価するための解析的検討を行った。岩盤中で臨界が起こる燃料成分の量の最小値を評価するための中性子輸送モデル(地下水飽和した球形の体系を想定して解析を実施)と、燃料成分の地下水中への溶出と岩盤中での移行を評価するための物質輸送モデルによる解析結果を組み合わせて評価を行った。その結果、燃料成分が岩盤中で蓄積する条件として保守的な条件を想定する場合では、臨界が起こる量が蓄積される状況も想定されるものの、処分場での使用済燃料の配置を工夫することで、こうした状況は起こりにくくなると考えられた。
Matheus Carnevali, P. B.*; Schulz, F.*; Castelle, C. J.*; Kantor, R. S.*; Shih, P.*; Sharon, I.*; Santini, J.*; Olm, M. R.*; 天野 由記; Thomas, B. C.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 10, p.463_1 - 463_15, 2019/01
被引用回数:48 パーセンタイル:88.33(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The metabolic platform in which microbial aerobic respiration evolved is tightly linked to the origins of Cyanobacteria (Oxyphotobacteria). Melainabacteria and Sericytochromatia, close phylogenetic neighbores to Oxyphotobacteria comprise both fermentative and aerobic representatives, or clades that are capablee of both. Here, we predict the metabolisms of Margulisbacteria from two distinct environments and Saganbacteria, and compare them to genomes of organisms from the related lineages. Melainabacteria BJ4A obtained from Mizunami site are potentially able to use O and other terminal electron acceptors. The type C heme-copper oxygen reductase found in Melainabacteria BJ4A may be adapted to low O
and other terminal electron acceptors. The type C heme-copper oxygen reductase found in Melainabacteria BJ4A may be adapted to low O levels, as expected for microaerophilic or anoxic environments such as the subsurface. Notably, Melainabacteria BJ4A seems to have a branched electron transport chain, with one branch leading to a cytochrome d ubiquinol oxidoreductase and the other one leading to the type C heme-copper oxygen reductase. Both these enzymes have high affinity for O
levels, as expected for microaerophilic or anoxic environments such as the subsurface. Notably, Melainabacteria BJ4A seems to have a branched electron transport chain, with one branch leading to a cytochrome d ubiquinol oxidoreductase and the other one leading to the type C heme-copper oxygen reductase. Both these enzymes have high affinity for O , thus are adapted to low O
, thus are adapted to low O levels. These contemporary lineages have representatives with fermentative H
levels. These contemporary lineages have representatives with fermentative H -based metabolism, lineages capable of aerobic or anaerobic respiration, and lineages with both. Our findings support the idea that the ancestor of these lineages was an anaerobe in which fermentation and H
-based metabolism, lineages capable of aerobic or anaerobic respiration, and lineages with both. Our findings support the idea that the ancestor of these lineages was an anaerobe in which fermentation and H metabolism were central metabolic features.
metabolism were central metabolic features.
奥村 雅彦; Kerisit, S.*; Bourg, I. C.*; Lammers, L. N.*; 池田 隆司*; Sassi, M.*; Rosso, K. M.*; 町田 昌彦
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 189, p.135 - 145, 2018/09
被引用回数:63 パーセンタイル:87.43(Environmental Sciences)東京電力福島第一原子力発電所事故により、環境中に放出された放射性セシウムは土壌中の粘土鉱物に強く吸着されていることがわかっているが、その吸着メカニズムは今も解明されていない。本論文は、これまで蓄積された粘土鉱物による放射性セシウム吸着現象に関する実験結果と、最新のシミュレーション研究の進展をまとめたものである。論文では、実験結果についてまとめられ、それらの結果を基にした最新のシミュレーション研究によって明らかにされた、次のような研究結果について説明されている:(1)粘土鉱物表面におけるセシウム吸着のエネルギースケール、(2)実験では観測が難しい粘土鉱物エッジの原子レベル構造についての理解の進展、(3)粘土鉱物の水和した層間におけるセシウム吸着現象の詳細、(4)ほつれたエッジにおけるイオン半径と層間距離の関係と吸着の選択性、(5)層間におけるセシウムの深部への移動、(6)放射性セシウムの核崩壊の影響。さらに、これらの知見に基づいた除染による廃棄土壌の減容技術開発の可能性についても述べられている。
Atz, M.*; Liu, X.*; Fratoni, M.*; Ahn, J.*; 平野 史生
Proceedings of 2017 International High-Level Radioactive Waste Management Conference (IHLRWM 2017) (CD-ROM), p.608 - 614, 2017/04
After nuclear waste is buried in a repository, hydrogeological processes can dissolve, transport, separate, and rearrange radionuclides inside or outside the repository. If fissile material becomes separated from neutron absorbers and precipitates in a far-field geologic formation, a critical mass may be formed. The scope of this study is to assess the impact of the spent fuel composition and host rock type on the risk of criticality in the far field. In particular, this study performs neutronics analysis in order to determine the minimum theoretical mass of fissile material needed to achieve criticality in a water-saturated far-field deposition under conservative conditions. Understanding of the effects of composition of spent fuels and host rock types enable discussion of the likelihood of far field criticality from LWR used fuel. In addition, this work makes recommendations on repository design and LWR fuel cycle management so as to minimize the risk of far-field criticality.
Liu, X.*; Fratoni, M.*; Ahn, J.*; 平野 史生
Proceedings of 2017 International High-Level Radioactive Waste Management Conference (IHLRWM 2017) (CD-ROM), p.595 - 599, 2017/04
The present work aims to study the effect of random geometry on the long-term criticality safety. Preliminary considerations on uranium depositions in randomly fractured rocks have been obtained through an approximated analytical solution to calculate spherical fuel lumps with random locations. With stochastic and heterogeneous conditions applied, the present work examines the conservatives of the neutronic models for repository criticality safety assessment, and provides deeper understandings of the system. The major finding is that, when parameters are chosen to optimized the criticality, effective multiplication factor for systems with the random geometries can be well-bounded by the average case.
Salazar, A.*; Fratoni, M.*; Ahn, J.*; 平野 史生
Proceedings of 2017 International High-Level Radioactive Waste Management Conference (IHLRWM 2017) (CD-ROM), p.600 - 607, 2017/04
The safety assessment of a geological repository for used nuclear fuel must ensure that future generations are shielded from radiation from fission products, in particular those released by re-criticality events. An investigation is required to understand whether or not criticality can actually be achieved. In fulfilling this end, this study assesses the uncertainty in the composition and total mass of precipitates forming in the far-field due to variation in transport parameters. The Latin Hypercube Sampling technique is employed to generate an accurate, random distribution of variables employed in the transport model and to assess the uncertainty of attaining a critical mass. The average characteristics of the damaged fuel from the Fukushima Daiichi reactor cores is used as the reference waste form. Results are compared to the minimum critical masses of previous studies to assess the criticality safety margin.
 and metal transformations associated with novel bacteria and archaea in deep terrestrial subsurface sediments
and metal transformations associated with novel bacteria and archaea in deep terrestrial subsurface sedimentsHernsdorf, A. W.*; 天野 由記; 宮川 和也; 伊勢 孝太郎; 鈴木 庸平*; Anantharaman, K.*; Probst, A. J.*; Burstein, D.*; Thomas, B. C.*; Banfield, J. F.*
ISME Journal, 11, p.1915 - 1929, 2017/03
被引用回数:107 パーセンタイル:96.15(Ecology)地層処分システムにおける微生物影響の可能性を評価するために、北海道の幌延深地層研究センター地下施設を利用して、堆積岩地下の生態系における微生物群集構造と代謝機能について調査を行った。全体として、微生物生態系は多様な系統群からなる微生物種で構成されており、その多くはこれまで培養されていない生物門に属していることが示された。大部分の微生物種は、酸化型[NiFe]ヒドロゲナーゼあるいはフェレドキシンをベースとする代謝経路を可能にする電子分岐型[FeFe]ヒドロゲナーゼを介して水素代謝をおこなうことが明らかになった。水素代謝と関連して、多くの微生物が炭素,窒素,鉄および硫黄を代謝することが推定された。特に、ANME-2dというメタン酸化を行う古細菌として知られている未培養微生物が、鉄関連の代謝反応を行う可能性が示唆された。得られた結果から、幌延堆積岩環境における微生物群集の生態学的概念モデルを推定した。
Hug, L. A.*; Baker, B. J.*; Anantharaman, K.*; Brown, C. T.*; Probst, A. J.*; Castelle, C. J.*; Butterfield, C. N.*; Hernsdorf, A. W.*; 天野 由記; 伊勢 孝太郎; et al.
Nature Microbiology (Internet), 1(5), p.16048_1 - 16048_6, 2016/05
被引用回数:1378 パーセンタイル:99.96(Microbiology)生命の系統樹は生物学において最も重要な中心テーマの一つである。遺伝子調査によると、莫大な数のブランチの存在が示唆されているが、フルスケールに近い系統樹でさえわかりにくいのが現状である。本研究では、これまでに報告されてきた配列情報に加えて、新たに取得した未培養生物のゲノム情報を用いて、バクテリア,アーキア,真核生物を含む系統樹を更新した。系統樹の描写は、全体的な概容とそれぞれの主要な系統における多様性のスナップショットの両方について行った。その結果、バクテリアの多様化の優勢性が示され、培養されていない生物種の重要性とともに主要な放射構造においてそれらの生物種の重要な進化が集中している現象が強調された。
Liu, X.*; Ahn, J.*; 平野 史生
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 52(3), p.416 - 425, 2015/03
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:16.04(Nuclear Science & Technology)The present study focuses on neutronic analysis to determine the criticality conditions for uranium depositions in geological formations resulting from geological disposal of damaged fuels from Fukushima Daiichi reactors. MCNP models are used to evaluate the neutron multiplication factor (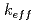 ) and critical mass for various combinations of host rock and geometries. It has been observed that the
) and critical mass for various combinations of host rock and geometries. It has been observed that the 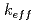 of the deposition become greater with (1) smaller concentrations of neutron-absorbing materials in the host rock, (2) larger porosity of the host rock, (3) heterogeneous geometry of the deposition, and (4) greater mass of uranium in the deposition. The present study has revealed that the planar fracture geometry applied in the previous criticality safety assessment for geological disposal would not necessarily yield conservative results against the homogeneous uranium deposition.
of the deposition become greater with (1) smaller concentrations of neutron-absorbing materials in the host rock, (2) larger porosity of the host rock, (3) heterogeneous geometry of the deposition, and (4) greater mass of uranium in the deposition. The present study has revealed that the planar fracture geometry applied in the previous criticality safety assessment for geological disposal would not necessarily yield conservative results against the homogeneous uranium deposition.
Liu, X.*; Ahn, J.*; 平野 史生
Proceedings of 14th International High-Level Radioactive Waste Management Conference (IHLRWMC 2013) (CD-ROM), p.527 - 534, 2013/04
本研究では溶融燃料を地層処分した場合の臨界安全性に注目し、MCNPモデルで仮定する地層中でのウランとプルトニウムの析出物の幾何学的形状の影響について検討した。東京電力福島第一原子力発電所の炉内溶融燃料を地層処分することを想定して、多様なパラメータに対して保守的な数値解析を実施した結果、臨界状態を生起させる系の条件の組合せが存在することが観察された。また、鉄を多く含む母岩の場合は臨界の可能性が顕著に低減できることが示された。
村上 冶子*; Ahn, J.*
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/10
This paper presents a new radionuclide transport model for performance assessment and design of a geologic repository for high-level radioactive wastes. The model applies compartmentalization and a Markov-chain approach. A model space consists of an array of compartments, among which radionuclide transport is described by a transition probability matrix. While the model is similar to Eulerian methods, the advantages of this approach are considered in flexibility in including various types of transport processes by probabilistic interpretation. We demonstrate this model approach with a hypothetical repository assumed in porous rock formation. A three-dimensional, non-uniform groundwater flow field is generated numerically by the finite element method. The transition probability matrix is constructed based on the velocity field and hydraulic dispersion coefficients. The results show that this transport model can effectively show differences in repository performance due to the change of hydraulic properties in the domain for differing repository configurations and material degradation.
池上 哲雄; Ahn, J.*
JAEA-Research 2006-045, 17 Pages, 2006/07
地層処分との関係において、分離変換の対象核種と分離変換の程度に関する目標設定に資することを目的に、従来の高レベル廃棄物そのものの潜在的放射性毒性に代わり、処分場での長寿命核種の移行挙動を考慮した新たな指標である「環境影響」を導入して、PWRサイクル及びFBRサイクルについて評価を行った。評価にあたって必要となる長寿命核種の廃棄物固化体への初期装荷量は廃棄物処理(conditioning)モデルを用いて求めた。環境影響を評価すると同時に、処分場内での核種移行挙動にかかわる各種パラメータの不確かさが環境影響に及ぼす影響も評価した。その結果、分離変換の目標は次のように設定できると考えられる。(1)PWRサイクルの場合:本評価で想定した廃棄物への移行率:U:0.604%, Pu:0.297%に加え、 Np,
Np,  Am, (
Am, ( Pu)の移行率を1%以下に抑える。(2)FBRサイクルの場合:全アクチニドに対するサイクルシステムとしての回収率99.9%は適切な設定である。
Pu)の移行率を1%以下に抑える。(2)FBRサイクルの場合:全アクチニドに対するサイクルシステムとしての回収率99.9%は適切な設定である。
Ahn, J.*; Rob, D. A.*; Kuo, S.*; Cha, P.L.*
PNC TY1952 98-001, 37 Pages, 1998/07
None